Understanding prototype cnc machining cost is essential for engineers and product designers who need accurate, functional prototypes without committing to full production tooling. CNC machining offers fast turnaround, high precision, and multi-material compatibility, making it one of the most reliable methods for early-stage development. This guide explains the major cost factors, material choices, and how to estimate your total prototype manufacturing budget.
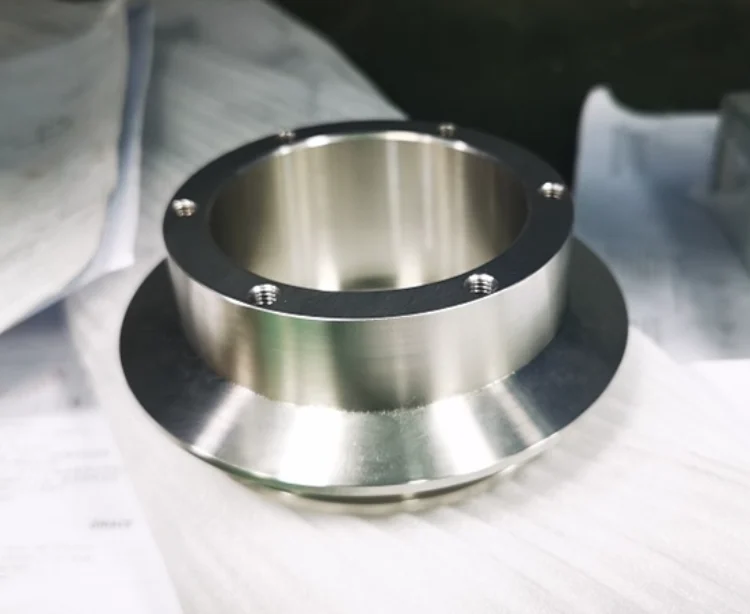

What Determines Prototype CNC Machining Cost?
The prototype cnc machining cost varies depending on geometry, machining time, tolerance requirements, materials, and finishing processes. Because prototypes often require unique one-off setups, understanding these cost influences helps designers optimize budgets.
1. Part Complexity and Machining Time
More complex shapes require additional toolpaths and programming time. Prototypes with thin walls, deep pockets, internal channels, or multi-sided structures increase machining hours—directly affecting cnc machining prototype cost.
2. Tolerances and Surface Requirements
Tight tolerances such as ±0.02 mm or high-polish surfaces take longer to achieve. Medical, optical, and robotics prototypes often have stricter requirements, raising the total prototype cnc machining cost.
3. Quantity and Batch Size
Since prototype CNC machining often involves single-piece or small-batch orders, setup costs cannot be distributed across many units. Ordering 5–20 pieces usually reduces per-unit pricing.
4. Material Selection
Different materials significantly affect pricing. Below is a quick overview of typical material choices and how they influence prototype cnc machining cost.
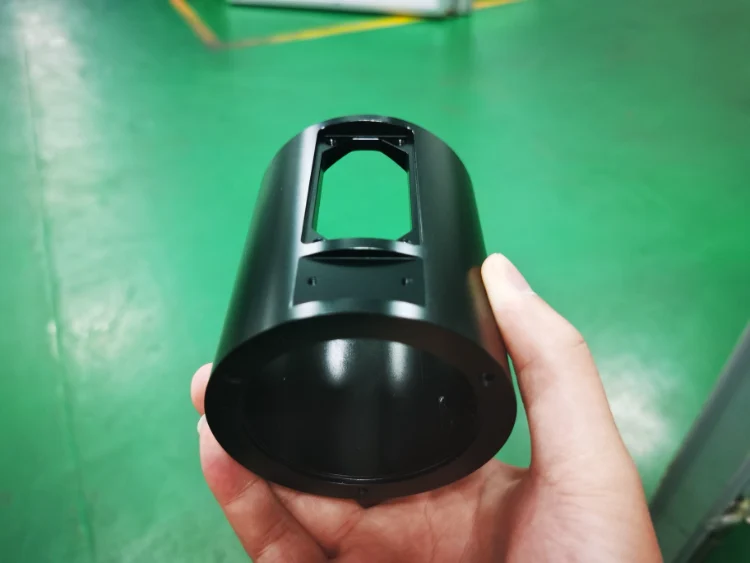

Material Options and Their Impact on Prototype CNC Machining Cost
Selecting the right material impacts machining speed, tool wear, and surface finishing—all contributing to the final price.
Metal Materials for CNC Prototype Machining
Aluminum Prototypes (6061, 5052, 7075)
aluminum cnc machining prototype parts are among the most affordable metal options due to excellent machinability and fast cutting speeds. Ideal for:
- Mechanical housings:CNC aluminum machining is ideal for mechanical housings such as motor, gearbox, and pump housings due to aluminum’s lightweight, strength, and good machinability. CNC processes allow complex internal cavities, mounting features, and precision bearing seats to be integrated into one part, ensuring good structural rigidity, high assembly accuracy, and stable performance, while also supporting tight tolerances and efficient production.
- Structural test samples:CNC aluminum machining is widely used to produce structural test samples for strength, fit, and reliability verification. Compared with casting or molding, CNC machining can directly produce test parts from solid material with high dimensional accuracy and consistent material properties, making it ideal for fast design validation, iteration, and performance testing in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
- Electronics components:CNC aluminum machining is commonly used for electronics enclosures, frames, and heat sinks thanks to aluminum’s excellent heat dissipation and EMI shielding. CNC machining enables thin-wall structures, precise interfaces, and clean appearance, meeting both functional and aesthetic requirements for products such as communication equipment, servers, and consumer electronics.
Aluminum is often chosen for cost-sensitive projects requiring structural integrity.
Stainless Steel Prototypes
More difficult to machine compared to aluminum, stainless steel raises prototype cnc machining cost due to slower cutting speeds and higher tool wear. Commonly used in:
- Medical device prototypes:Stainless steel CNC machining is widely used for medical device prototypes due to its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and biocompatibility. It is suitable for surgical instruments, test fixtures, structural components, and equipment housings that require high precision and clean surface quality. CNC machining allows tight tolerances and fine details, making it ideal for functional testing, assembly verification, and pre-production validation.
- Wear-resistant components:Stainless steel is an ideal material for wear-resistant components because of its high hardness, toughness, and long-term stability under friction and load. CNC machining can produce precise contact surfaces, shafts, sleeves, and guide components with consistent quality and good surface finish. These parts are commonly used in industrial equipment, automation systems, and mechanical transmission structures where durability and reliability are critical.
- High-strength assemblies:Stainless steel CNC prototypes are often used in high-strength assemblies that must withstand heavy loads, vibration, or harsh environments. The material provides excellent mechanical strength and structural stability, while CNC machining ensures accurate interfaces and reliable assembly fit. This makes it suitable for applications such as equipment frames, support structures, and critical mechanical modules.

Brass and Copper
Excellent for electrical testing prototypes. However, copper may increase machining cost because of its softness and heat conduction.
Electrical & Conductive Components:Brass and copper offer excellent electrical conductivity and stable electrical performance, making them ideal for various conductive and contact components. CNC machining can produce high-precision terminals, connectors, busbars, and contact parts, ensuring accurate dimensions and high-quality contact surfaces. These components are widely used in power equipment, charging systems, and industrial electrical assemblies.
Thermal Management Components:Copper has extremely high thermal conductivity, making it especially suitable for heat sinks, heat spreaders, and liquid cooling plates. CNC machining allows the integration of complex flow channels, thin-wall structures, and high-precision mounting interfaces, significantly improving heat dissipation efficiency. These components are commonly used in electronic devices, power modules, and high power-density equipment.
Precision Mechanical & Decorative Parts:Brass and copper feature good machinability, corrosion resistance, and attractive surface appearance, making them suitable for precision mechanical parts and decorative components. CNC machining can produce valves, fittings, bushings, and parts with high appearance requirements, ensuring excellent surface quality and dimensional consistency. They are widely used in instrumentation, piping systems, high-end hardware, and precision equipment.
Plastic Materials for CNC Prototype Machining
Plastics offer lightweight and lower-cost alternatives, depending on project needs.
ABS
Easy to machine and low-cost, ideal for design housings and fixtures.
Housings & Enclosures: ABS is widely used for equipment housings, control boxes, and electronic enclosures due to its good strength, toughness, and low cost. CNC machining allows complex outer shapes, mounting bosses, and internal rib structures. It is suitable for non-load-bearing or medium-strength structural applications in industrial and consumer products.
Fixtures & Test Parts: ABS is commonly used for fixtures, jigs, and prototype parts for structure and assembly verification. It is easy to machine and cost-effective, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and small-batch iteration. It can also be used as auxiliary parts for long-term use under light load conditions.
Covers & Panels: ABS is suitable for protective covers and decorative panels that require a balance between appearance and basic structural strength. CNC machining ensures dimensional accuracy and good assembly consistency. It is often used for equipment covers and external panels.
POM/Delrin
High stiffness and low friction, suitable for mechanical movement prototypes.
Gears, Bushings & Sliding Parts: POM has excellent wear resistance and self-lubricating properties, making it ideal for gears, bushings, and sliding components. CNC machining ensures precise mating dimensions and good surface finish, improving stability and service life. It is widely used in automation equipment and mechanical transmission systems.
Precision Functional Parts: POM is commonly used for positioning parts, clips, connectors, and functional structural components that require good dimensional stability. The material has high rigidity and low deformation, making it suitable for parts that must maintain accuracy over long-term use. CNC machining provides high repeatability and stable batch consistency.
Automation Components: POM is widely used for guide parts, support parts, and mechanism components in automation equipment. It offers a good balance between strength, wear resistance, and machinability, and is suitable for medium-load and long-term operating mechanisms.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Transparent material requiring polishing, slightly increasing cnc plastic machining prototype cost.
Transparent Covers & Windows: PC offers high transparency and excellent impact resistance, making it ideal for viewing windows, protective covers, and transparent housings. CNC machining ensures precise shapes and reliable mounting structures. It is widely used in industrial equipment and automated production lines.
Protective Housings: PC is suitable for safety guards and equipment protection structures that require both visibility and impact resistance. Compared with ordinary plastics, PC is much less likely to crack under impact. It is commonly used in equipment with safety protection requirements.
Structural & Functional Parts: PC can also be used for parts that require both strength and toughness. CNC machining allows the integration of mounting features, ribs, and functional structures. It is suitable for parts that require structural strength together with certain appearance or transparency requirements.
PEEK
High-performance engineering plastic that significantly raises prototype cnc machining cost due to raw material expense and machining difficulty.
High-performance Structural Parts: PEEK has extremely high mechanical strength and excellent high-temperature resistance, making it suitable for aerospace and high-end equipment structural components. It can operate reliably for long periods in harsh and high-temperature environments. CNC machining ensures high precision and reliable assembly performance.
Medical & Semiconductor Components: PEEK offers excellent chemical resistance, thermal stability, and good biocompatibility, and is widely used in medical and semiconductor equipment. It is commonly used for insulation parts, support parts, and structural components. CNC machining meets the requirements for high cleanliness and high precision.
High-wear & High-temperature Parts: PEEK is often used for gears, bushings, and support parts in high-temperature or high-wear environments. Compared with metal, it helps reduce weight, eliminate lubrication, and lower noise. It is ideal for applications with extremely high reliability and service life requirements.
Typical Price Range for Prototype CNC Machining Cost
Pricing varies but typical ranges include:
| Prototype Type | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| Simple plastic prototypes | $20–$80 |
| Aluminum CNC prototypes | $50–$200 |
| Stainless steel prototypes | $80–$300 |
| PEEK or engineering plastic prototypes | $100–$500 |
| Complex multi-side machining prototypes | $200–$800+ |
These prices depend heavily on geometry and finishing.
Additional Cost Factors in CNC Prototyping
1. CAM Programming
High-quality CAM programming plans reasonable toolpaths, cutting sequences, and machining strategies, which directly determine whether the dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and geometric tolerances of CNC prototypes can meet requirements.
By scientifically setting cutting parameters, collision-avoidance strategies, and material allowance distribution, tool wear can be reduced, and the risks of tool breakage and part deformation can be minimized, thereby improving machining stability and first-pass yield.
Optimized toolpaths reduce air cutting, enable efficient roughing and precise finishing, significantly shorten prototype machining cycles, and help control costs, meeting the core needs of rapid verification and iterative development during the product R&D stage.
2. Tooling and Fixturing
Fixtures directly determine the positioning accuracy and clamping stability in CNC prototyping. Improper fixtures can cause part misalignment or deformation, leading to out-of-tolerance dimensions and geometric errors. Well-designed fixtures enable fast and accurate positioning, reduce setup time, and ensure consistency between the first piece and repeat inspections, forming the foundation for achieving required prototyping accuracy.
High-quality fixtures simplify the clamping process and reduce setup difficulty, helping to avoid issues such as chatter, tool chipping, or part movement caused by improper fixturing, thereby improving machining stability and first-pass yield. At the same time, they can flexibly adapt to the multi-variety and small-batch nature of prototyping, shorten setup and iteration cycles, and balance efficiency with cost control.

3. Finishing and Post-Processing
Finishes that may increase prototype cnc machining cost:
- Sanding or polishing:a physical finish process that uses sandpaper, abrasives, or polishing wheels to remove machining marks, burrs, and surface imperfections, resulting in a smoother and more uniform appearance. Depending on the process grade, it can achieve finishes ranging from matte to near mirror-like gloss. It also provides an even base surface for subsequent treatments such as anodizing or passivation.
- Anodizing:mainly used for aluminum alloys and magnesium alloys, which forms a dense protective oxide layer on the metal surface. This oxide layer significantly improves wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and scratch resistance. It can also be dyed into black, silver, or various colors, combining both protective and decorative functions.
- Passivation:A chemical treatment process that removes free iron, contaminants, and oxides from the surface of stainless steel and other metals, forming a uniform and stable chromium-rich passive film. This process does not change the part’s dimensions or appearance color. Its main purpose is to enhance corrosion resistance and extend service life in humid or corrosive environments.
- Laser marking:Laser marking uses a high-energy laser beam to permanently mark logos, part numbers, specifications, QR codes, and other information on the surface in a non-contact process. The markings are clear, wear-resistant, and not easy to fade or peel off. It offers high precision and requires no consumables, making it suitable for permanent marking on metals and some plastics.
- Assembly and threading:The process of machining internal threads in pre-drilled holes to accommodate bolts, studs, and other fasteners, while assembly refers to combining and fastening multiple components into a complete product according to drawings. This stage belongs to the final post-machining and integration process. It directly affects assembly accuracy, joint strength, and overall functional performance.
- Surface smoothing for plastics:For plastic parts produced by injection molding or CNC machining, surface smoothing is performed through sanding, bead blasting, or chemical polishing to remove parting lines, tool marks, burrs, and surface roughness. This process improves surface touch and visual consistency. It also helps reduce defects in subsequent processes such as painting or silk-screen printing and enhances the overall product appearance.
4. Lead Time
Rush orders can increase pricing due to priority machine scheduling.This requires prioritizing production, working overtime, and compressing production processes. To meet tight delivery deadlines, the processing plant may need to invest in more machinery and engineering resources, thereby increasing operating and labor costs. More flexible delivery schedules help optimize processes and plan resources more effectively, thus effectively controlling overall processing costs.

Applications That Depend on Prototype CNC Machining
Electronics
- Device housings
- Sensor brackets
- Heat sink simulations
Medical Devices
- Surgical tool prototypes
- Diagnostic housings
- Ergonomic test handles
Robotics
- Gear systems
- Alignment blocks
- Functional arms and joints
Automotive & Aerospace
- High-load mechanical components
- Lightweight aluminum prototypes
- Fluid system test parts
For all these industries, understanding prototype cnc machining cost allows teams to efficiently plan development cycles.

How to Reduce Prototype CNC Machining Cost
Optimize Design
Optimizing the design can simplify structures and reduce difficult-to-machine features such as complex surfaces, deep slots, and undercuts, thereby lowering the difficulty of CNC programming and machining. Reducing complex curved surfaces and narrow-space machining not only shortens toolpath time but also decreases the risk of tool breakage and rework. This helps reduce machining hours and tool consumption at the source.
Choose the Right Material
ABS or aluminum can drastically reduce cnc machining prototype cost compared to stainless steel or PEEK.Selecting a cost-effective material based on the actual performance requirements of the prototype helps avoid unnecessarily using expensive special materials, directly reducing raw material costs. Choosing materials that are easy to machine and widely used can also reduce cutting resistance, extend tool life, and improve machining efficiency. This indirectly lowers machine time and post-processing costs.
Standardize Tolerances
Set reasonable tolerances according to the actual functional requirements of the prototype instead of blindly pursuing ultra-high precision. This reduces unnecessary finishing operations and repeated adjustments. More relaxed but compliant tolerances simplify the process flow, reduce inspection costs and scrap rates, and avoid extra expenses such as high-rigidity machines and precision tools required for overly tight tolerances.
Order Small Batches Instead of One Piece
Producing small batches can spread fixed costs such as programming, tool setup, fixture adjustment, and machine warm-up, making the cost per part much lower than producing a single prototype. Batch machining also helps stabilize process parameters and improve first-pass yield, reducing material and tool waste caused by trial cutting. In addition, having spare parts for further R&D iterations avoids repeated setup costs in future runs.

Conclusion
Choosing a reliable manufacturer is critical for achieving accurate prototypes at reasonable cost. As an experienced supplier of prototype cnc machining cost solutions, Weldo provides precision machining for both metal and plastic prototypes, transparent pricing, and professional engineering support. Whether you need simple design samples or complex functional prototypes, our team can help optimize cost, material selection, and manufacturing efficiency.
Contact Weldo today for competitive pricing and expert consultation regarding any prototype CNC machining cost requirements.
FAQ of prototype cnc machining cost
What is prototype CNC machining cost influenced by?
Key factors include part complexity, material type, tolerance requirements, machining time, and finishing needs.
Are aluminum prototypes cheaper than steel prototypes?
Yes. Aluminum is faster to machine and often lowers cnc machining prototype cost significantly.
How much do plastic CNC prototypes typically cost?
Plastic prototypes usually range from $20–$80 depending on geometry and finishing needs.
Why is CNC machining preferred over 3D printing for prototypes?
CNC machining provides higher accuracy, better mechanical strength, and materials identical to final production.

