An as machined finish is one of the most common surface conditions produced directly from CNC machining processes. In many industrial applications, an machined finish offers an optimal balance between functionality, accuracy, and cost. Understanding when and how to use an machined finish helps engineers and buyers make informed manufacturing decisions without unnecessary secondary operations.
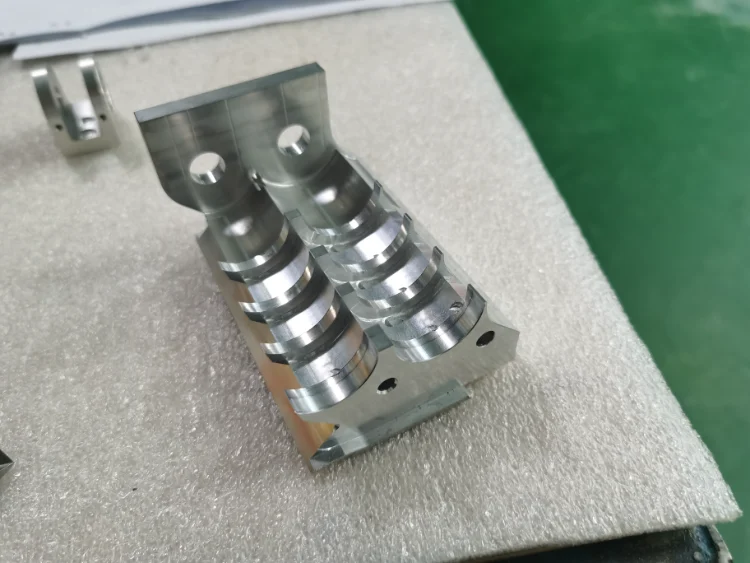
What Is an As Machined Finish?
An machined finish refers to the surface condition of a part immediately after CNC milling, turning, or drilling, without any additional surface treatment. The surface texture is determined by cutting tools, machining parameters, and material properties.
In most cases, an machined finish exhibits visible tool marks and a consistent, functional surface suitable for mechanical assembly and industrial use.
Typical surface roughness for an machined finish:
- Ra 1.6–3.2 μm (63–125 μin), depending on material and tooling
How an As Machined Finish Is Achieved
An machined finish is produced through controlled CNC operations rather than secondary finishing processes. Key factors influencing the final appearance include:
- Tool geometry and sharpness
- Cutting speed and feed rate
- Toolpath strategy
- Material machinability
A skilled CNC machining service provider ensures that an machined finish meets functional and dimensional requirements while maintaining efficiency.

Materials Suitable for As Machined Finish
Many engineering materials perform well with an machined finish, making it a versatile surface option.
Metals Commonly Using Machined Finish
- Aluminum alloys (6061, 7075, 2024)
- Stainless steel (304, 316, 17-4PH)
- Carbon steel and alloy steel
- Brass and copper
- Titanium alloys
These metals maintain stable dimensions and acceptable surface quality with an machined finish, especially for structural or internal components.
Plastics Suitable for As Machined Finish
- POM (Delrin)
- ABS
- Nylon
- PTFE
- PEEK
For many plastic components, an as machined finish is sufficient for functional testing and final use.

Advantages of As Machined Finish
Choosing an machined finish offers several practical benefits.
Cost Efficiency
An machined finish eliminates secondary finishing steps such as polishing, coating, or anodizing, reducing overall machining cost.
Fast Lead Time
Because no post-processing is required, parts with an machined finish can be produced and delivered faster.
Dimensional Accuracy
Secondary surface treatments may alter part dimensions. An as machined finish preserves original machining tolerances.
Functional Performance
For internal components, fixtures, brackets, and industrial parts, an machined finish provides sufficient surface quality without added expense.
Limitations of As Machined Finish
Despite its advantages, an machined finish is not suitable for every application.
Visible Tool Marks
An machined finish typically shows machining marks, which may not meet aesthetic requirements for visible parts.
Limited Corrosion Protection
Without coatings or treatments, an as machined finish offers minimal corrosion resistance, especially for steel components.
Surface Roughness Constraints
Applications requiring ultra-smooth surfaces may need polishing or grinding instead of an machined finish.
Understanding these limitations helps determine when an as machined finish is appropriate.

As Machined Finish vs Other Surface Finishes
Compared with anodizing, polishing, or bead blasting, an machined finish focuses on function rather than appearance.
- Machined finish: cost-effective, fast, functional
- Anodized finish: corrosion resistance, color options
- Polished finish: smooth appearance, decorative
- Bead blasted finish: matte texture, reduced glare
A CNC machining service provider can recommend the right finish based on application needs.
Typical Applications of As Machined Finish
An machined finish is widely used across industries, including:
- Industrial equipment components
- Automotive and EV parts
- Aerospace structural parts
- Medical device prototypes
- Fixtures, jigs, and tooling
In these applications, performance and precision matter more than cosmetic appearance.
When to Choose an As Machined Finish
An machined finish is the best choice when:
- Parts are internal or non-visible
- Tight tolerances are required
- Cost and lead time are critical
- Parts will receive secondary processing later
Early consultation with a CNC machining service provider ensures optimal surface selection.

Why Choose Weldo Machining for As Machined Finish Parts
Weldo Machining provides precision CNC machining with reliable machined finish quality across metals and plastics. Our engineers optimize machining parameters to deliver consistent surface quality while controlling cost and lead time.
As a trusted CNC machining service provider, we support customers with:
- Material-specific machining strategies
- Tight tolerance control
- Prototype and production scalability
- Transparent quoting and fast turnaround
Conclusion: As Machined Finish for Practical CNC Applications
An as machined finish remains one of the most practical and widely used surface options in CNC machining. It offers cost efficiency, fast delivery, and reliable dimensional accuracy for a broad range of materials and applications.
If your project requires functional, precision CNC parts without unnecessary finishing cost, contact Weldo Machining today to discuss machined finish options and receive a competitive quotation.


