Auto parts precision manufacturing increasingly demands higher consistency, shorter lead times, and lower total landed cost; auto cnc machining is often the core method for achieving high-precision mass production. This article explains the definition, importance, typical parts, process collaboration, and supplier selection criteria for auto parts cnc machining, helping you accelerate automotive part manufacturing and improve go-to-market execution.
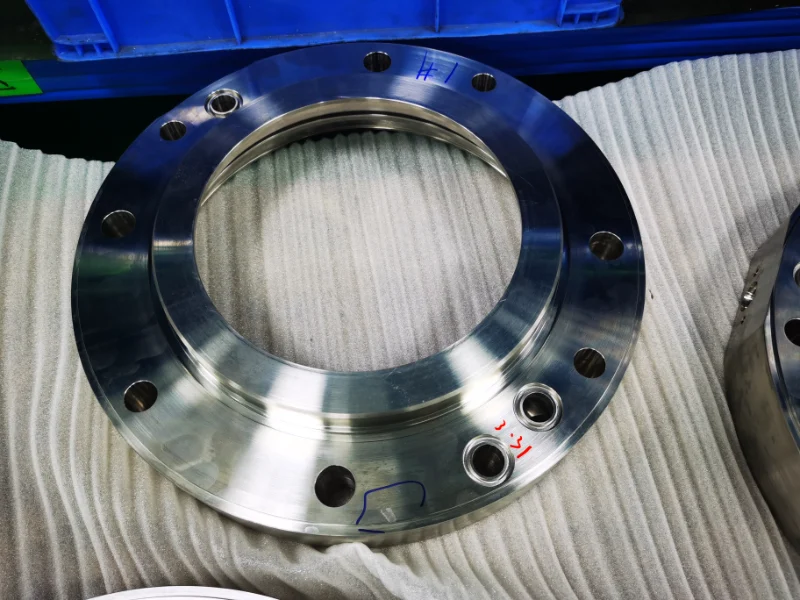

Definition: What Is Auto CNC Machining?
Auto cnc machining refers to a CNC manufacturing system designed specifically for automotive components. It typically uses CNC turning, milling, drilling/tapping, boring/reaming, and grinding as the primary processes, and combines fixtures, tooling strategies, in-process measurement, and SPC to meet automotive requirements for dimensions, tolerances, surface treatment, and traceable delivery—enabling long-term stability in volume production.
Why Auto CNC Machining Matters
Consistency and Safety
Key characteristics such as hole location, sealing surfaces, and coaxiality require stable machining control. cnc machined auto parts can significantly improve machining accuracy and standardization.
Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Toolpath optimization, tool-life management, automated loading/unloading, and operation consolidation make auto cnc machining more cost-competitive in mass production—reducing manual involvement while enabling semi-automated, high-standard production.
Faster Ramp-Up
When transitioning from prototypes to pilot runs and then to mass production, the approach supports process validation, gaging plans, and traceability in parallel—shortening the validation cycle for auto cnc machining.
Better Fit for New Energy Vehicles
E-drive and thermal-management components are more complex. cnc machined auto parts is better able to balance complex geometries with precision, supports rapid iteration, and helps reduce tooling/mold costs.

Typical Auto CNC Machined Parts (Examples)
Common cnc machined auto parts include:
Powertrain / Drivetrain
Bushings, end caps, spline/shaft parts, and partially machined housing features.
Chassis / Steering / Braking
Control arm brackets, subframes, bushings, ball-joint seats, and hub-related machined parts.
E-Drive / Thermal Management
Motor end caps, electronic control housings, cooling plates, valve bodies, and pipeline fittings.
Structures and Assembly
Aluminum connectors, hinge components, locating pins, and fasteners such as screws.
These parts generally rely on consistent datums, hole-pattern quality, and deburring quality—so they are well-suited to stable delivery through auto part cnc machining and batch-level traceability.
Main Processes in Auto CNC Machining and How They Work Together
A typical auto cnc machining routing (tailored to part features) includes:
Turning to Establish Datums
First establish coaxial/face datums to provide reliable locating for subsequent milling and hole-pattern machining in auto cnc machining.
Milling Forming (3/4/5-Axis)
Machine cavities, steps, and surfaces. Five-axis machining reduces manual part re-clamping/adjustment and improves both accuracy and efficiency—making it a key enabler for high-efficiency car parts cnc machining.
Hole-Making Chain
Drilling → enlarging → reaming/boring to ensure hole diameter, roundness, and positional tolerance, forming a stable hole system and strengthening assembly consistency in auto cnc machining.
Threading
Tapping or thread milling. Thread milling improves chip breaking and dimensional controllability, making it suitable for volume car component cnc machining.
Finishing and Post-Processing
If needed, grinding/honing; then deburring, cleaning, and surface/heat treatment to close the loop on assembly safety and corrosion resistance.
Collaboration Key Points
Prioritize datum establishment, machine rough-to-finish, and complete as many features as possible in a single setup. Use in-process measurement and SPC as a closed loop to stabilize both yield and takt time—so consistency becomes repeatable in auto cnc machining.

How to Choose the Right Auto CNC Machining Supplier
When evaluating an auto cnc machining supplier (outsourcing/partnering), consider five areas:
Capability and Equipment
Turn-mill integration, 4/5-axis capacity, automation, and in-process measurement—plus proven auto cnc machining cases and mature process packages.
Quality System
IATF/ISO, MSA/SPC, first-article/in-process/final inspection, traceability, and PPAP/FAI delivery capability—whether the supplier meets automotive-grade requirements for auto cnc machining.
Engineering Support
Ability to provide DFM suggestions, routing design, inspection plans, and fast prototyping—hard requirements for importing auto cnc machining, and critical for subsequent mass production.
Delivery and Integration
Whether material sourcing, heat treatment, surface treatment, and fixture responsiveness are controllable—and whether stable supply can be maintained during ramp-up for auto cnc machining.
Cost Transparency and Continuous Cost-Down
Clear cost breakdowns, plus continuous optimization of cycle time, tooling, and operation consolidation to support long-term, cost-controlled auto cnc machining cooperation.
Conclusion and Inquiry
The value of auto parts cnc machining is not only “making parts,” but systematizing process, quality, and delivery so that parts can be produced consistently and repeatably at scale. If you need project-fit process recommendations, sample validation, or mass-production quotations for automotive parts, you are welcome to contact Weldo Machining. Send your drawings, materials, and tolerance requirements—we will quickly evaluate risk points and cost structure, and provide more detailed information and pricing to support your high-standard auto parts program.