A PMMA CNC machining quote is essential for industries that require transparent, high-precision acrylic parts for medical devices, optics, electronics, and industrial equipment. Because PMMA offers excellent clarity and rigidity, the machining process requires controlled speed, optimized feed rate, sharp cutting tools, and proper cooling. Understanding how PMMA material grade, tool geometry, machining parameters, and finishing requirements affect a PMMA CNC machining quote helps buyers reduce cost and achieve top-quality results.
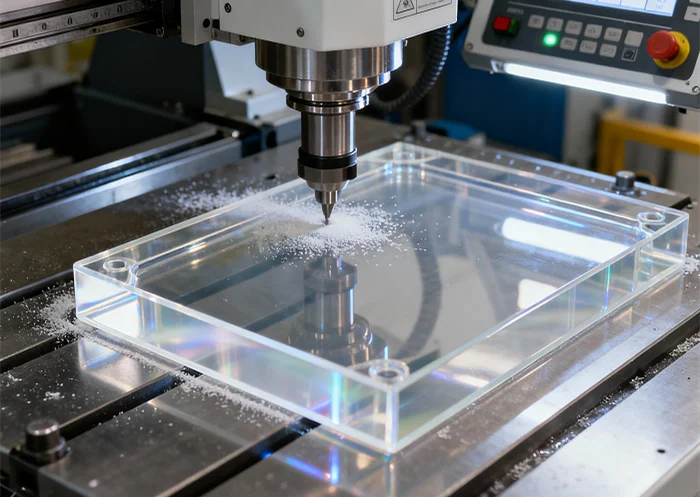

PMMA Material Pros and Cons (Impact on PMMA CNC Machining Quote)
Advantages of PMMA
- High optical clarity
Ideal for lenses, windows, and light guides. Clearer surfaces often increase polishing needs, influencing the PMMA CNC machining quote. - Rigid and dimensionally stable
Excellent for structural housings and mechanical sliders. - Lightweight and easy to machine
Chips cleanly with the right tools and feed rate. - Good weather and UV resistance
Suitable for outdoor indicators, panels, and protective covers.
Disadvantages of PMMA
- Lower impact resistance vs. polycarbonate
Risk of cracking under heavy load or incorrect clamping. - Heat-sensitive
Melts or chips if spindle speed and feed are not optimized, affecting machining time and PMMA CNC machining quote. - Poor chemical resistance
Cannot be exposed to certain solvents during cleaning or finishing. - Surface easily scratches
Often requires polishing, increasing finishing cost.
Understanding these characteristics helps determine the correct machining strategy and avoid unnecessary cost.
How Material Grade Affects Your PMMA CNC Machining Quote
Cast PMMA
- Highest clarity
- Better for polishing
- Better dimensional stability
Used for optical lenses and precision components; typically increases PMMA CNC machining quote.
Extruded PMMA
- More economical
- Easier to machine at higher feed rates
Ideal for covers, panels, housings. Offers a lower PMMA CNC machining quote.
Impact-Modified PMMA
- Tougher but less transparent
- Requires slower speeds and stronger tools
Used for protective screens and casings. Raises machining cost due to tool wear.

Machining Speeds, Feed Rates & Cutting Parameters
Optimal Spindle Speeds
- 18,000–24,000 rpm for small tools
- 10,000–16,000 rpm for medium end mills
High rpm improves clarity but demands cooling to avoid melting.
Feed Rate Guidelines
- Finish passes: 0.03–0.10 mm/tooth
- Roughing: 0.10–0.25 mm/tooth
Balanced feed prevents edge chipping and lowers PMMA CNC machining quote.
Depth of Cut
- Roughing: 0.5–1× tool diameter
- Finishing: 0.1–0.3 mm
Shallow finishing passes provide near-polished surfaces.
Cutting Tool Selection for PMMA
Single-Flute Carbide End Mills
- Best for high-speed cutting
- Excellent chip clearing
- Stable heat control
O-Flute Bits
- Polished cutting edges
- Designed for PMMA clarity
- Reduce polishing time, improving PMMA CNC machining quote efficiency
Diamond-Coated Tools
- Necessary for optical-grade components
- High durability
- Lower scrap rate despite higher cost
Tool Geometry Tips
- High rake angle
- Ultra-sharp edges
- Low helix design
These minimize heat and micro-cracking.
Common Surface Finishing Options for pmma cnc machining part
PMMA (acrylic) requires careful finishing to achieve optical clarity or cosmetic-grade appearance. Each finishing option improves functionality but also influences the total machining cost.
1. Flame Polishing
What it does:
Uses controlled flame to melt the micro-surface, restoring transparency and smoothness.
Pros:
- Fast and cost-effective
- Very clear finish on external edges
Cons:
- Not suitable for internal pockets
- Can slightly warp thin-walled PMMA if overheated
Price impact:
Adds 10–20% to total cost depending on edge length and complexity.
2. Vapor Polishing (Solvent Polishing)
What it does:
Chemical vapor smooths the PMMA surface and increases optical clarity.
Pros:
- Best for optical parts
- Produces nearly glass-like transparency
Cons:
- Requires special equipment and experienced operator
- Not suitable for stress-prone designs
Price impact:
Adds 20–40% because of material preparation, controlled environment, and post-fixturing.
3. Mechanical Polishing (Buffing / Sanding)
What it does:
Uses fine abrasive tools to manually or semi-automatically polish surfaces.
Pros:
- Best for flat or accessible surfaces
- Can remove machining marks completely
Cons:
- Labor-intensive
- Hard to apply to internal cavities
- May not achieve 100% optical clarity like vapor polishing
Price impact:
Adds 15–35% depending on surface area and required smoothness.
4. Bead Blasting (Matte Finish)
What it does:
Creates a matte, frosted surface on PMMA.
Pros:
- Aesthetic satin finish
- Hides machining marks
- Good for consumer electronic housings
Cons:
- Reduces transparency
- Can cause micro-pitting if pressure is too high
Price impact:
Adds 10–25%, depending on coverage.
5. Hard Coating / Anti-Scratch Coating
What it does:
Adds a protective layer to increase abrasion resistance.
Pros:
- Improves durability
- Reduces scratching
- Good for automotive displays and high-touch surfaces
Cons:
- Requires professional coating systems
- Higher cost than other treatments
Price impact:
Adds 30–60%, depending on thickness and curing process.
6. UV Coating / Anti-UV Layer
What it does:
Protects PMMA from yellowing and sun degradation.
Pros:
- Ideal for outdoor products
- Improves lifespan
Cons:
- Might slightly alter gloss level
- Additional curing required
Price impact:
Adds 15–30%.
7. Screen Printing / Laser Marking
What it does:
Adds text, logo, scales, or alignment marks.
Pros:
- Useful for displays or medical device windows
- Laser marking is permanent and precise
Cons:
- Extra processing steps
- Laser marking slightly frosts the surface
Price impact:
Adds $1–$5 per part depending on complexity.
How Surface Finishing Influences PMMA CNC Machining Cost
Surface finishing affects the overall PMMA CNC machining quote through:
1. Additional Labor
More polishing = more operator time.
2. Specialized Equipment
- Vapor polishing → high-cost chambers
- Hard coating → UV curing ovens or robotic spray systems
3. Part Preparation
PMMA must be cleaned, dried, and de-stressed before finishing.
4. Scrap Risk
Thin or complex parts may warp during polishing, increasing scrap cost.
5. Optical Requirements
The higher the clarity required → the more finishing passes needed.
Rule of Thumb:
Surface finishing can add 10–60%+ to the total machining price depending on the method and optical requirements.
Applications & PMMA CNC Part Types
Optical Components
- Lenses
- Light guides
- Diffusers
Need flame/vapor polishing for final clarity.
Electronics
- Transparent covers
- LED windows
- Display panels
Medical Devices
- Diagnostic windows
- Laser housings
- Protective shields
Industrial Equipment
- Machine guards
- Flow windows
- Inspection doors
Each application has unique tolerances and finishing needs that influence a PMMA CNC machining quote.
Cost Structure Behind a PMMA CNC Machining Quote
1. Material Cost
Cast PMMA is more expensive; extruded PMMA lowers cost.
2. Machining Time
Optical-grade parts require more finishing passes.
3. Tooling Cost
Diamond tools increase tool cost but reduce rework.
4. Finishing
Flame polishing/vapor polishing can add 10–40%.
5. Tolerances
- ±0.05–0.10 mm standard
- ±0.02–0.05 mm for optical features
More precision = higher PMMA CNC machining quote.
How to Reduce PMMA CNC Machining Quote
Improve Part Geometry
Avoid extreme thin walls, deep pockets, and sharp internal corners.
Choose the Right Grade
Extruded PMMA is ideal when optical precision isn’t required.
Use Proper Workholding
Reduces cracking and scrap, lowering machining cost.
Optimize Pass Strategy
More aggressive roughing + lighter finishing helps reduce cycle time.
Scale Your Order
Batch machining greatly reduces the unit price of a PMMA CNC machining quote.
Conclusion
A PMMA CNC machining quote depends on material grade, machining parameters, tooling choice, precision requirements, and finishing methods. Selecting the right PMMA material and optimizing machining strategies allow buyers to achieve high optical quality and strong mechanical performance at the best cost. For detailed technical support and fast quotations, contact Weldo Machining for professional PMMA machining solutions.
FAQ of pmma cnc machining
Does PMMA require coolant during machining?
Yes, coolant or air blast prevents melting and improves transparency.
Can PMMA be tapped directly for threaded holes?
Yes, but for repeated use, metal thread inserts are recommended.
What surface roughness can CNC achieve on PMMA?
Fine finishing can reach optical-grade Ra with correct tooling.

