Surface grinding
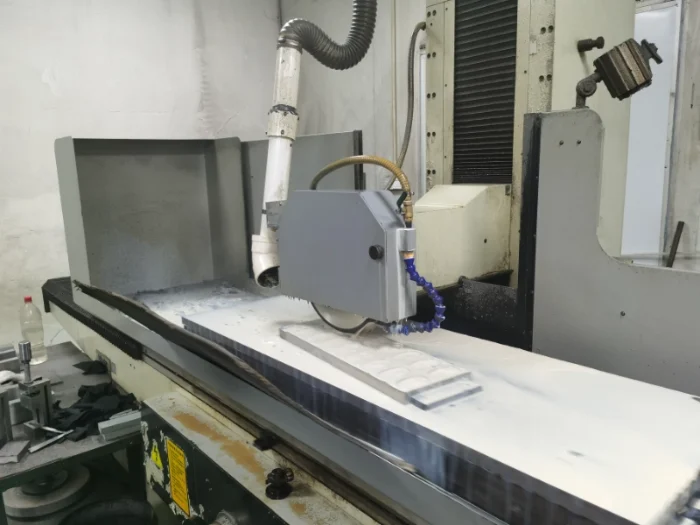

Overview
Whether you require single-piece customization, small-batch prototyping, or high-volume efficient production, we can tailor surface grinding processes (longitudinal/plunge/deep grinding, etc.) based on your workpiece drawings and technical specifications, with tolerances controlled to within 0.003mm.
What is surface grinding ?
Surface cylindrical grinding is a precision machining technique that uses grinding processes to process the outer cylindrical surfaces of workpieces. It effectively enhances dimensional accuracy, geometric accuracy, and surface finish. The core principle involves a rotating grinding wheel contacting the workpiece’s outer cylindrical surface to remove excess material and correct geometric errors, ultimately achieving a surface that meets design specifications.
Surface grinding material
Surface grinding is primarily used for machining metal materials, though it can also process certain plastic materials. However, there are differences in application scenarios and machining results.
Metal material :
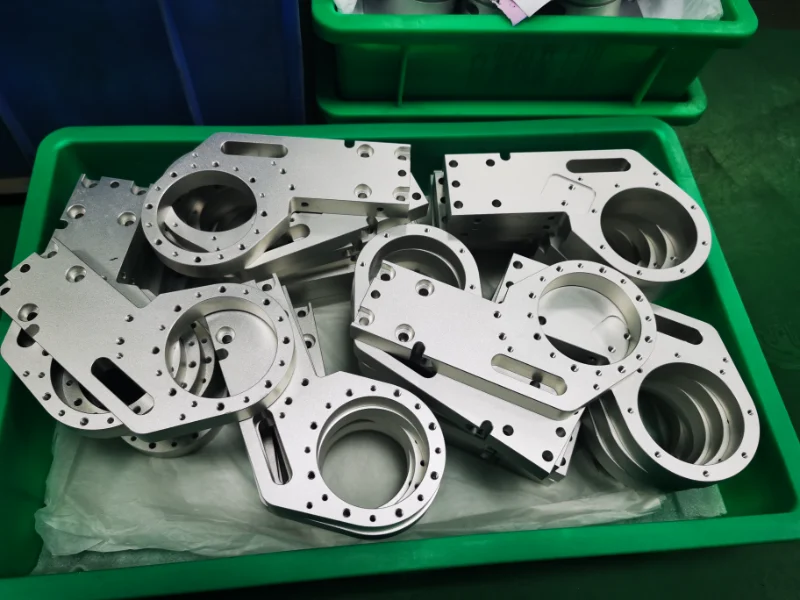

Aluminum
Aluminum is the most commonly used precision-machined component. It has a low density, a hard texture, and a soft material. Thanks to its corrosion resistance, it is widely used in aerospace, bionic bones, and automotive parts manufacturing.
Color : Silver.
Types : Aluminum 6061、7075、2024、5052、6063 and MIC-6.
Surface finish : Polishing, Brushing, Sandblasting, Chrome Plating, Anodizing, Electroplating, Powder Coating, Laser Etching.
Delivery time : 1-5 days.
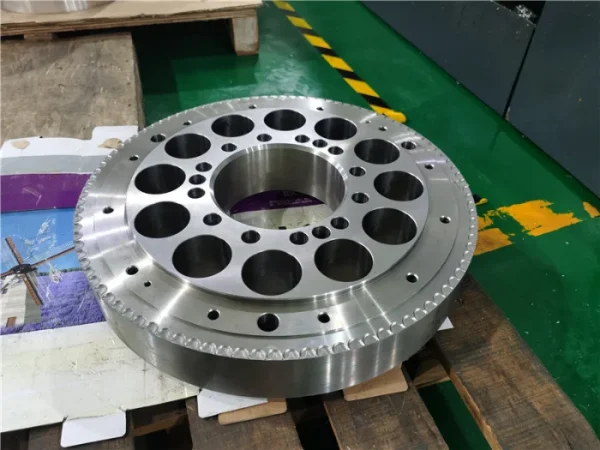

Stainless steel
Stainless steel offers strong corrosion resistance and a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It is primarily used in kitchen equipment components, medical devices, building materials and construction, as well as automotive parts.
Color : Silver.
Types : Stainless steel 304/316/201/202/430/444/410/420/440c/2205/2507/17-4ph/17-7ph.
Surface finish : Polishing, Brushing, Sandblasting, Electroplating, Spraying, PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition), Passivation, Pickling, Coloring.
Delivery time : 2-5 days.

Copper
Possesses electrical conductivity, tensile ductility, and antimicrobial properties, primarily used for processing into crafts, decorative items, and medical equipment.
Color :Orange,yellow.
Types : copper H59/H62/Hpb59-1/C36000/HAI77-2/HSN62-1/HPb/HMn/HAl/HSn/HNi.
Surface finish : Passivation, Electroplating, Chemical Plating, Shot Peening, Sandblasting, Chemical Film Treatment, Polishing, Bright Cleaning.
Delivery time : 1-5 days.
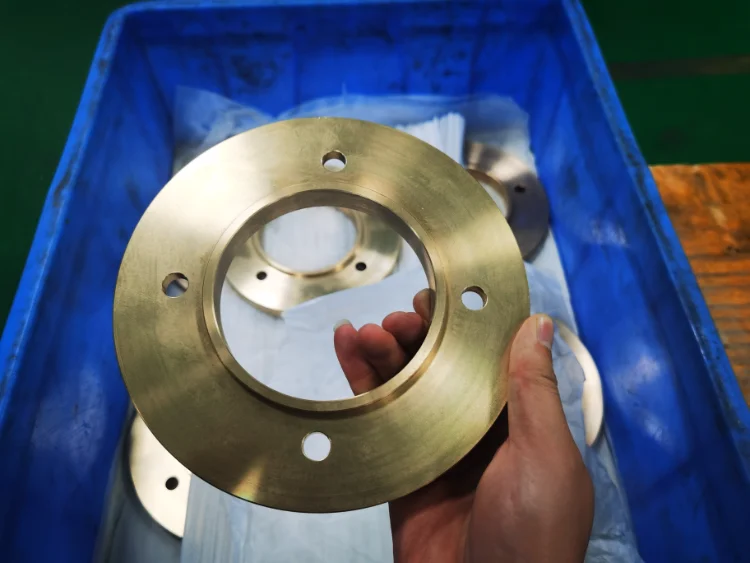

Bronze
Bronze is a copper–tin alloy with good fluidity and corrosion resistance. It is commonly used for bearings, gears, valves, sculptures, and marine components such as propellers and water pumps.
Color : gold/brown.
Types : Tin bronze, aluminum bronze, beryllium bronze, silicon bronze, manganese bronze.
Surface finish : Sandblasting, polishing, knurling, grinding, passivation, chemical film coating, impregnation coloring, brush/spray coloring, electroplating, anodizing, powder coating, brushing.
Delivery time : 1-5 days.
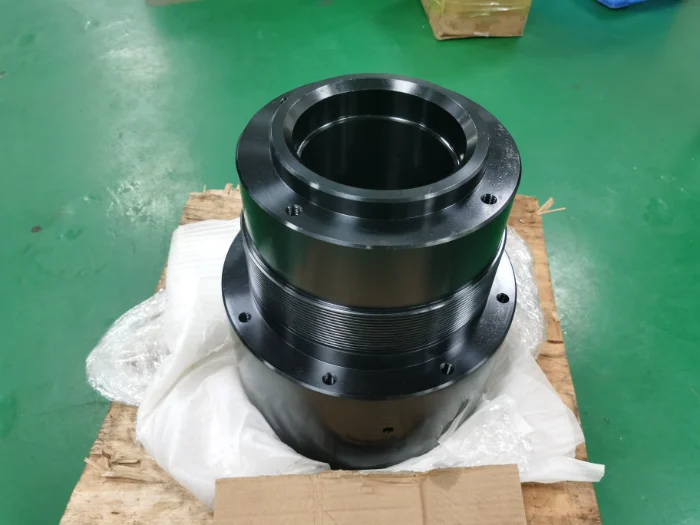

Steel
Steel is an iron–carbon alloy (0.1%–1.7% carbon) with added elements such as chromium and nickel. Through composition and heat treatment, it offers high strength, toughness, wear and corrosion resistance, and is widely used for bolts, shafts, gears, cutting tools, engine valves, and turbine blades.
Color : Silver .
Types : Steel S20C,S45C,S50C,SK85,SK95,40Cr,4140,4130,H13,D2,W1,A2,D2,M2,SKD11,ASP-23,S136.
Surface finish :Sandblasting, Mirror Finish, PVD Coating, Brushed Finish, Spray Coating, Electroplating.
Delivery time : 1-5 days
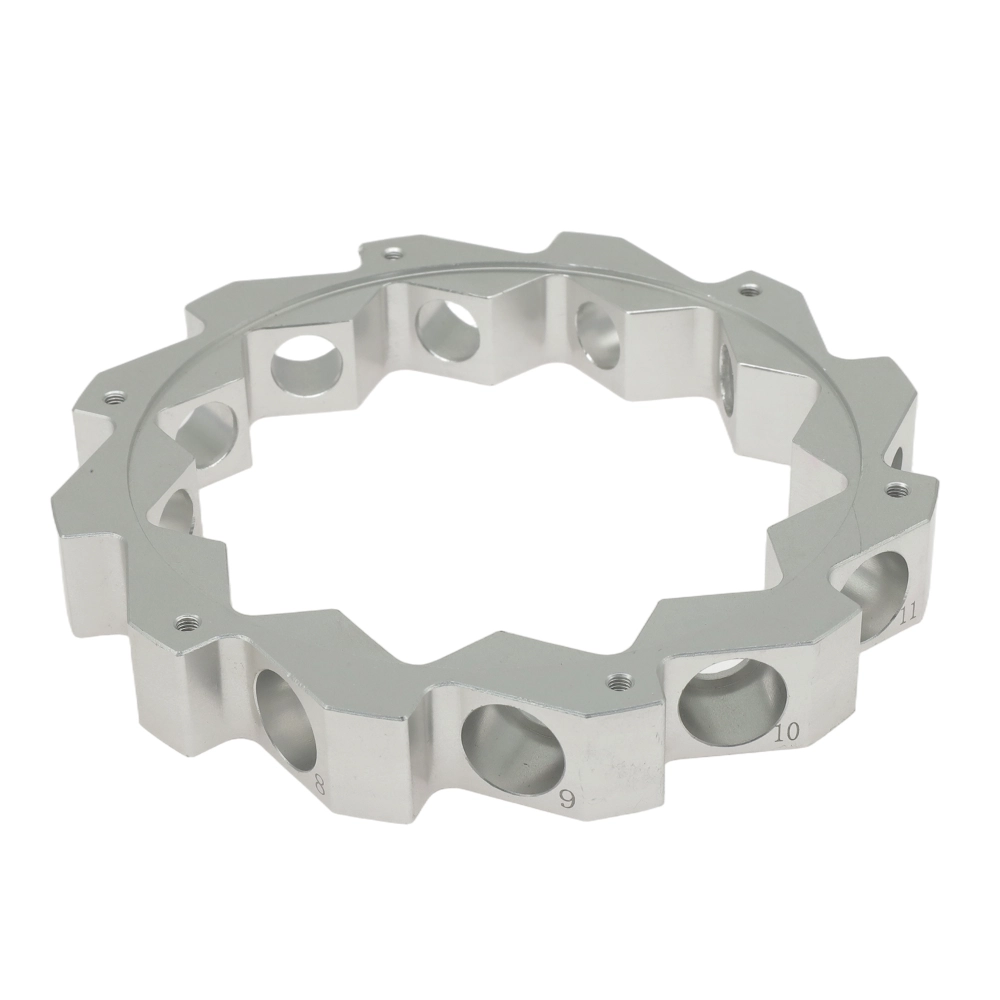

Magnesium
Magnesium is a lightweight metal with low cutting force, high thermal conductivity, and an excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Its superior vibration damping makes it suitable for aerospace, automotive, and electronics applications.
Color : Silver.
Types : Magnesium alloy AZ91D/AM60B/AM50A/AS41B/ZK60/MB8/AZ31/WE43/ZE41/LA141/LZ91.
Surface finish : Chemical conversion coating, anodizing, nickel plating, electroplating, composite coating, spray painting, powder coating, electrophoretic coating.
Delivery time : 1-5 days.
Surface grinding cnc machining capability
Our ISO 9001 certification demonstrates that our surface grinding parts meet stringent tolerance requirements. We adhere to ISO-2768f tolerance standards for metals and ISO-2768m for plastic parts, enabling you to obtain CNC-grinding components with high-precision machining standards.
| PROPERTY | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Maximum part size | The maximum direct machining diameter is 500mm, with a maximum machining length of 1000mm. For longer components requiring precision grinding, we can adjust the equipment accordingly. |
| Minimum part size | The diameter is as small as 3 mm, depending on the specific part size requirements and material. |
| General tolerance | Our CNC grinding standard tolerance is 0.005mm. If material and structure permit, tighter tolerances as low as ±0.001mm can be achieved. |
| Lead time | Prototype machining typically ships within 1-3 days. Small-batch CNC grinding takes 3-5 days, with the fastest turnaround possible within 24-48 hours depending on part complexity and material. |
Surface grinding machining guideline
To ensure stable accuracy and surface quality in CNC grinding, appropriate grinding wheel selection and process parameter control are essential. The following table provides a practical reference for CNC grinding parameters and wheel selection.
| CLASSIFICATION | PARAMETER / TYPE | SPECIFIC DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Grinding Wheel Selection | Grit Size | Rough grinding (stock removal > 0.1mm): 24–60 gritPrecision grinding (0.05–0.1mm): 60–100 gritSuper-precision grinding (special conditions): W63–W14 micro-powder |
| Hardness | For hard workpieces, use a grinding wheel 1–2 grades softer (e.g., HRC60 → H-grade wheel)For soft workpieces, use a wheel 1–2 grades harder (e.g., copper → K-grade wheel) | |
| Material | Aluminum oxide: for carbon steel and alloy steelSilicon carbide: for hard alloys and ceramicsDiamond: for non-ferrous metals and hard non-metal materials (not suitable for steel)CBN: for hardened steel and high-temperature alloys | |
| Bond | Ceramic bond: general-purpose grindingResin bond: suitable for high-speed grinding (>50m/s) | |
| Grinding Parameters | Speed | Normal grinding: 30–35m/sHigh-speed grinding: 50–150m/s (machine capability and cooling required) |
| Feed Rate | Longitudinal: 0.5–2 mm/r (upper limit for rough grinding, lower limit for precision grinding)Transverse: rough grinding 0.05–0.15 mm/pass, precision grinding 0.005–0.02 mm/pass | |
| Workpiece Speed | 10–30 m/min For hard or large-diameter workpieces (>200 mm or HRC > 50): reduce to 10–15 m/min | |
| Coolant | Flow Rate | Rough grinding: 20 L/min ,Precision grinding: 10 L/min |
| Pressure | 0.1–0.3 MPa (ensure coolant penetration into grinding zone) | |
| Type | Water-soluble: for rough grinding Oil-soluble: for precision grinding of non-ferrous metals |
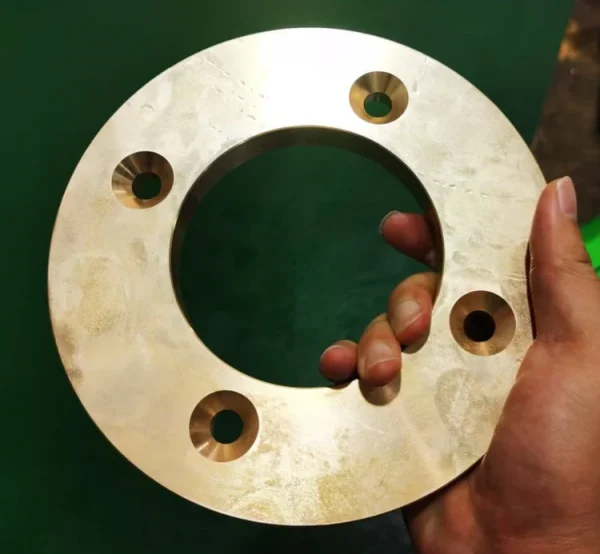
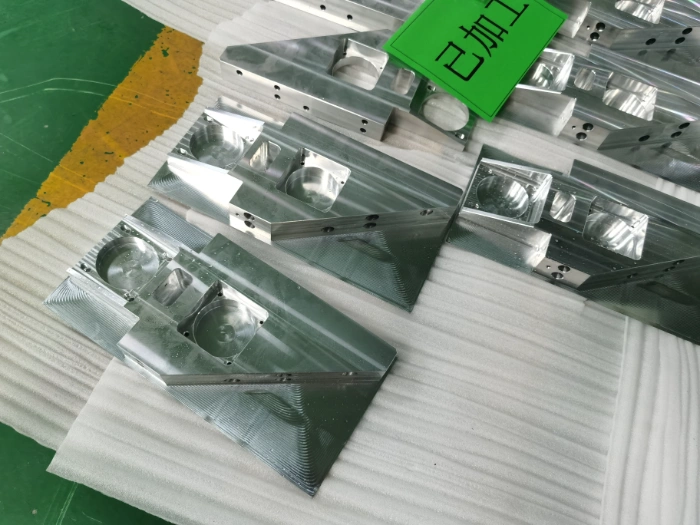
Surface grinding machining prototypes
Our surface grinding CNC machining services effortlessly handle complex curved surfaces and three-dimensional multi-faceted structures, covering plastics, metals, large (small) components, and large (small) batch production. Tolerance control precision reaches 0.005mm.
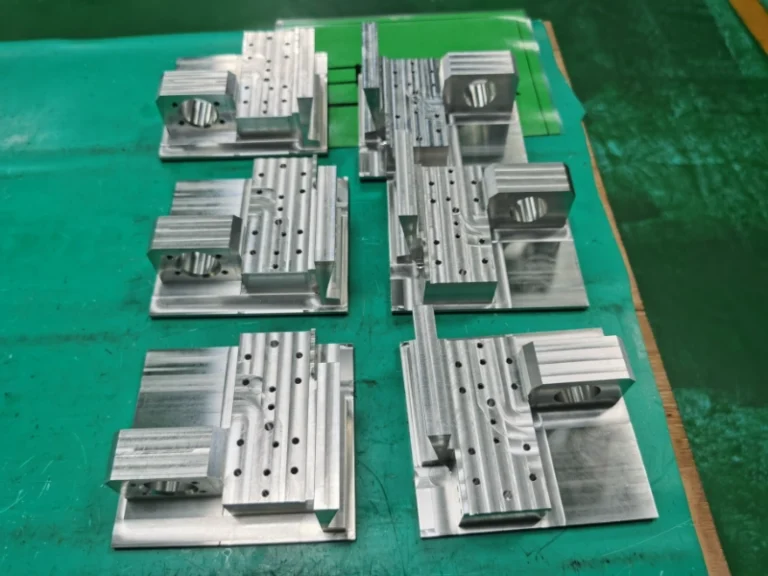
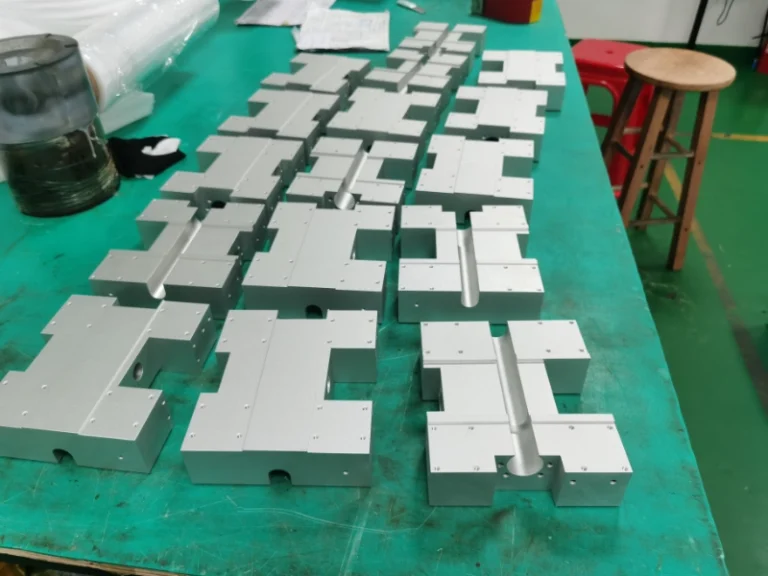
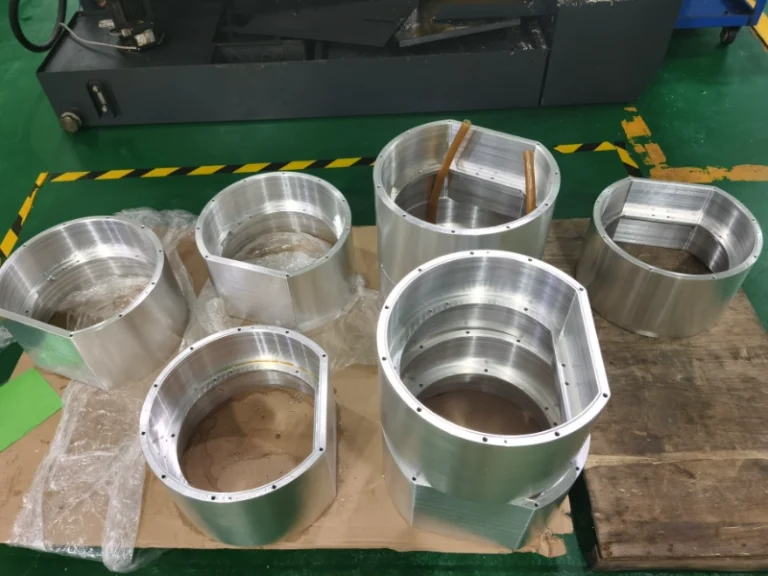
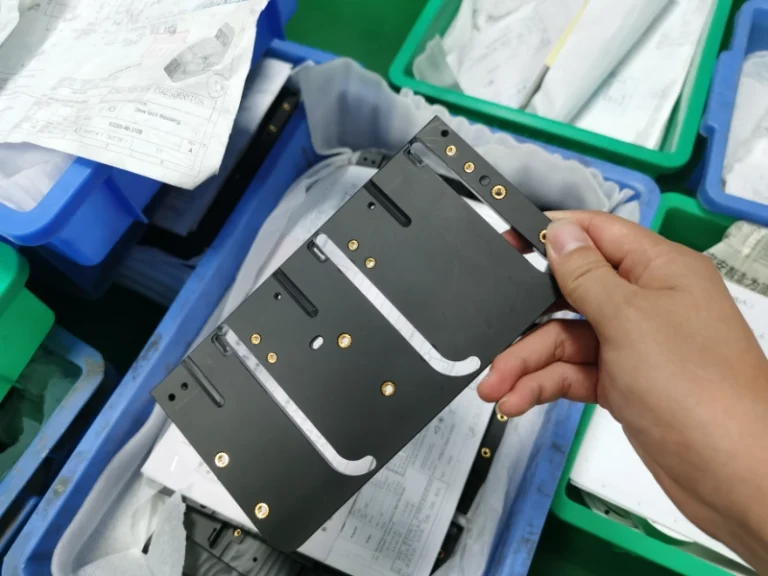
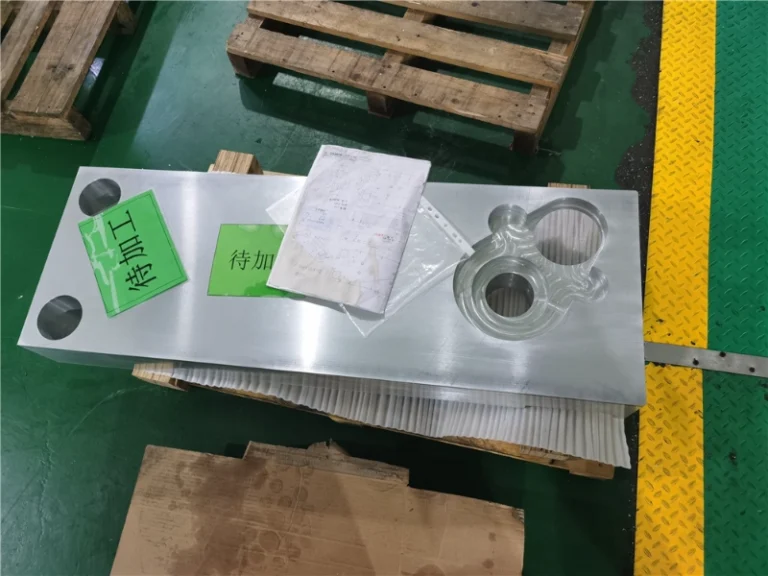






Advantage of surface grinding
1. High Precision
Machining accuracy achieves within ±0.005mm, with strict flatness and parallelism, suitable for high-fitment parts like molds and gauges.
2. Ultra-High Surface Finish
Surface roughness Ra values can reach below 0.1μm, meeting mirror-like finish requirements for optical components and hydraulic slides.
3. Rapid Material Removal
Rough grinding achieves feed rates exceeding 0.1mm per pass, swiftly removing excess material from castings/forgings to shorten mass production cycles.
4. Broad Material Adaptability
Through selection of grinding wheel materials (aluminum oxide, CBN, diamond, etc.), it can process various materials including steel, titanium alloys, ceramics, and cemented carbides.
5. Process Stability
CNC or automated equipment ensures machining consistency, minimizes human error, and is suitable for standardized parts in large-scale production.
Application of surface grinding part
1. Automotive Manufacturing:
Crankshafts, drive shafts, bearing rings
Ensures journal dimensional accuracy to IT5 grade (±0.005mm) and surface roughness Ra≤0.4μm, reducing friction loss and enhancing power transmission efficiency.
2. Aerospace:
Turboshafts, engine blades, landing gear struts
Machining nickel-based alloys and titanium alloys to achieve surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.1μm, meeting strength requirements under high-temperature, high-pressure conditions.
3. Energy Equipment:
Wind turbine main shafts, gas turbine rotors
Control taper error ≤0.01mm (wind turbine shafts) and dynamic balance accuracy ≤G1 grade (gas turbines) to withstand complex loads.
4. Precision Machinery:
Hydraulic spool valves, optical instrument shaft systems
Clearance fit 1-3μm (hydraulic spool valves), surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.025μm (optical shafts), reducing leakage rates.
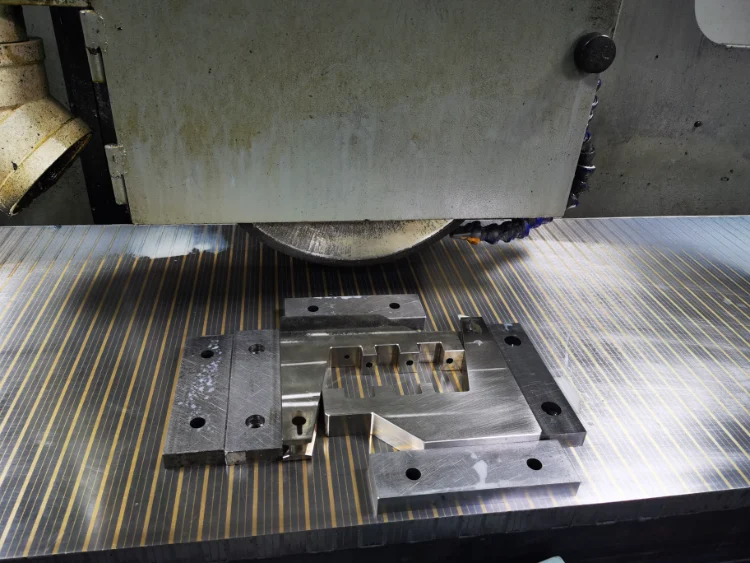
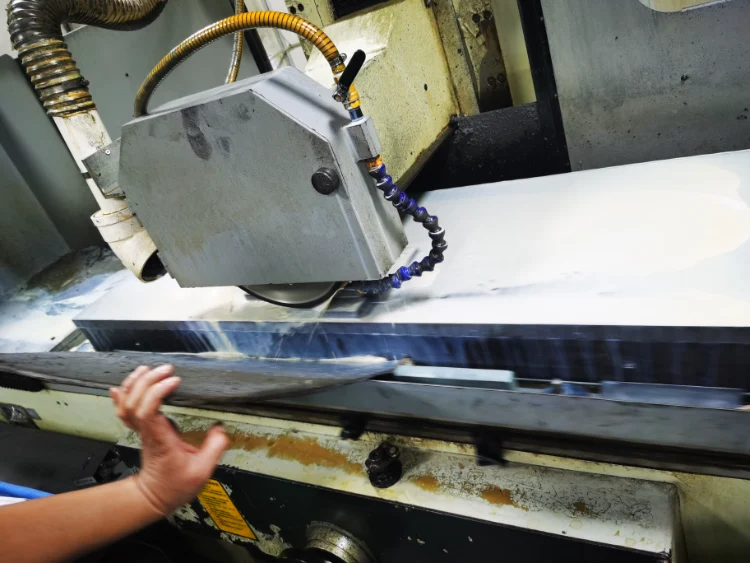
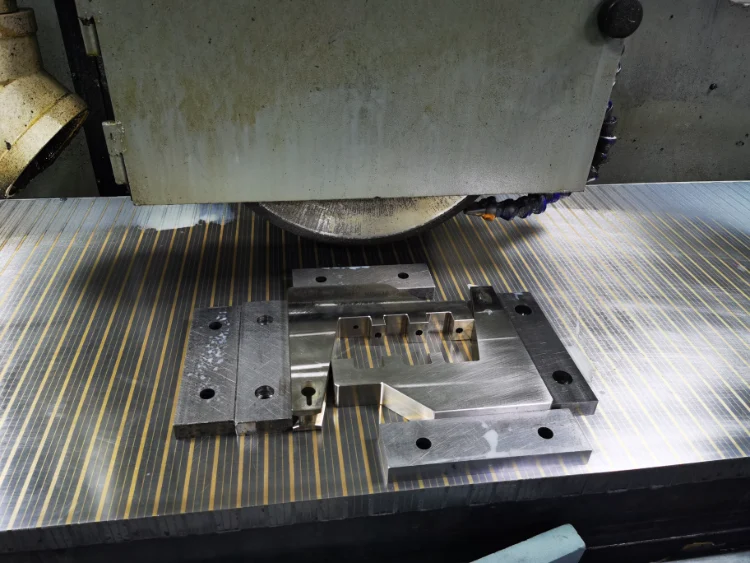



FAQ of cnc grinding
What materials can be machined by CNC grinding?
CNC grinding is suitable for hard and dimensionally stable materials, including carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, hardened steel, carbide, ceramics, and selected engineering plastics such as POM, PEEK, and filled nylon. Soft or heat-sensitive plastics are generally not recommended due to deformation risks.
What level of accuracy can CNC grinding achieve?
CNC grinding can typically achieve tolerances of ±0.005 mm, and under optimized conditions, tolerances as tight as ±0.001 mm are possible. Surface finishes can range from Ra 0.8 μm down to Ra 0.1 μm, depending on the grinding method and wheel selection.
When should CNC grinding be used instead of CNC milling or turning?
CNC grinding is preferred when parts require very tight tolerances, excellent surface finish, or machining of hardened materials. It is commonly used as a finishing process after milling or turning to improve dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
What factors affect surface quality in CNC grinding?
Surface quality in CNC grinding depends on grinding wheel selection, grit size, grinding speed, feed rate, coolant type, and thermal control. Proper parameter optimization and effective cooling are essential to prevent burns, chatter, and thermal deformation.

