Magnesium cnc machining
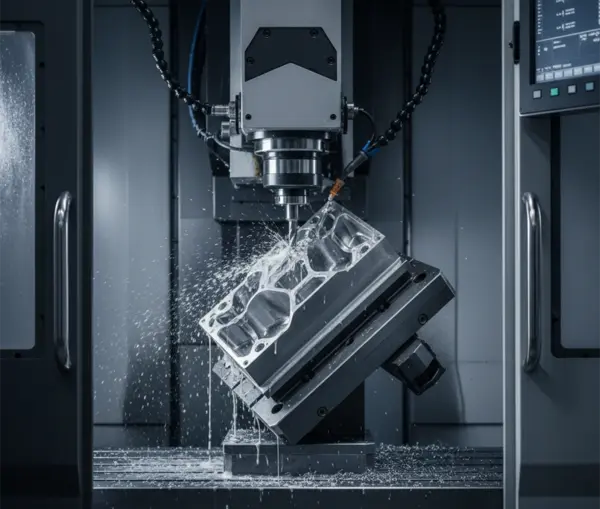

Overview
We have our own 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining centers, and our employees have an average of over 10 years of CNC machining experience.
Mass production standard tolerance: Linear dimensions ±0.05 mm. Unspecified tolerances follow ISO 2768-m by default.
Recommended tolerance grades: General assembly IT10–IT12, precision fits IT8–IT9. IT7 or tighter should not be committed lightly.
Thin-wall parts, large parts, and die-cast parts: Tolerances should be appropriately relaxed, typically ±0.05 to ±0.10 mm.
Surface roughness: Standard Ra 1.6–3.2 μm, fine finishing can reach Ra 0.8 μm.
Cost: 20~500 usd/PCs
Contact us for pricing and more information about magnesium CNC machining.
What is magnesium cnc machining ?
CNC machining of magnesium alloys uses computer-programmed CNC machine tools to perform cutting and other operations on magnesium alloys, which are 30% lighter than aluminum, to precisely manufacture parts. It is highly efficient, suitable for mass production, and achieves an accuracy of 0.005 mm. It can process complex structures with good surface quality and is commonly used in the 3C, automotive, and aerospace industries.
Common magnesium type for cnc machining
AZ91D Magnesium Alloy
Characteristics: High aluminum content (approximately 9%), outstanding strength and hardness, relatively low cost, making it one of the most widely used magnesium alloys. Its Knoop hardness (HK) reaches 76.2, and its corrosion resistance is superior to some aluminum alloys.
AZ31 Magnesium Alloy
Characteristics: Lower aluminum content (approximately 3%), good plasticity, but slightly lower strength and hardness than AZ91D (Knoop hardness HK is 51.1).
ZK60 Magnesium Alloy
Characteristics: High-strength magnesium alloy, suitable for load-bearing structures, good wear resistance, but relatively brittle, making it difficult to process.
Mg-Mn Alloys: Excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for parts in chemical equipment and humid environments.
Mg-RE Alloys: Contain rare earth elements, stable high-temperature performance, used in high-temperature engine components.
Mg-Li Alloys: Extremely low density, the lightest known metallic structural material, suitable for applications where weight is extremely sensitive (such as satellite components).
Surface finish for cnc machining magnesium part
Based on over 15 years of CNC machining experience, we have compiled the following list of surface finish processes used for various precision-machined parts made from magnesium material.
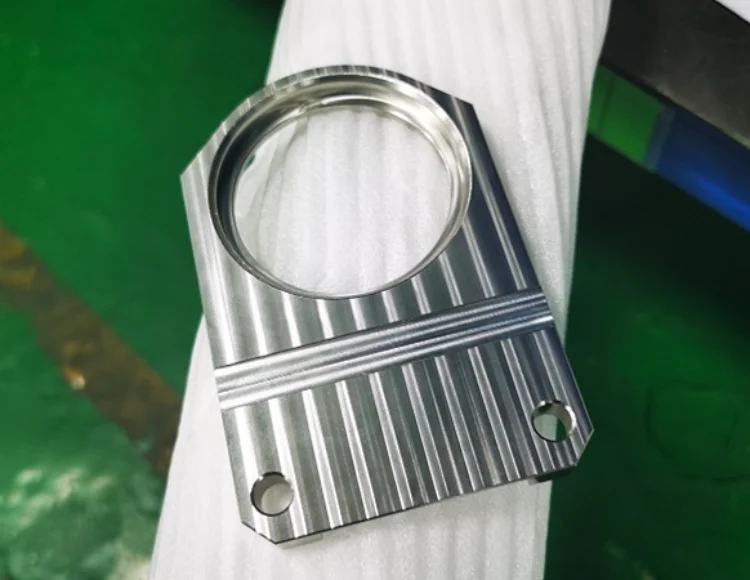

Machined finish
The prototype processed by the machine tool retains traces of tool machining.
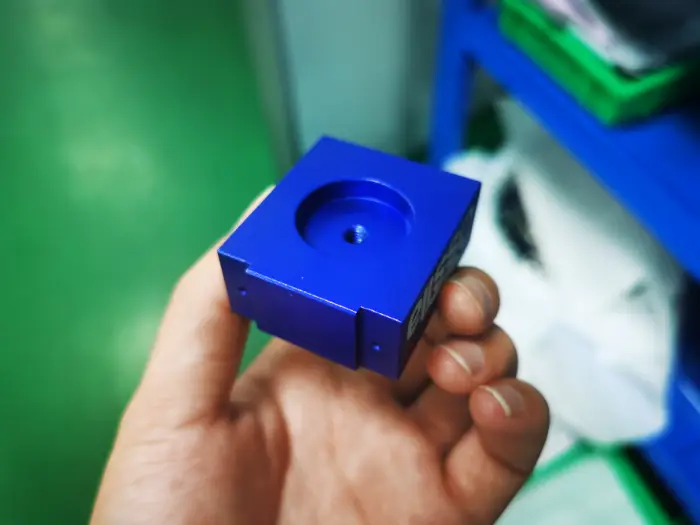

Anodizing
Anodizing enhances the corrosion and wear resistance of metals and enables coloring and coating, suitable for metals.
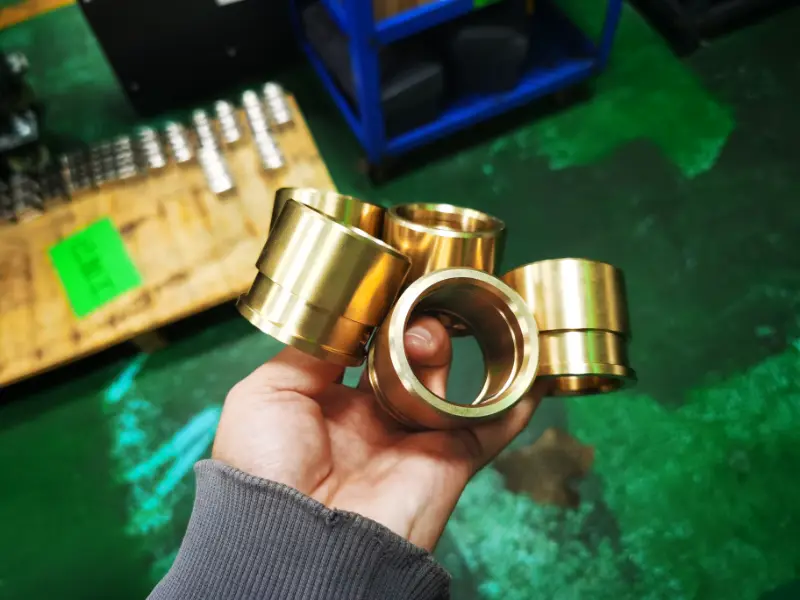

Polish
Polishing enhances surface finish and aesthetic appeal, suitable for materials such as metals, ceramics, plastics, and PMMA.

Sand blasting
Sandblasting involves propelling abrasive material at high pressure or mechanically onto a workpiece to achieve a clean, roughened, and matte finish.

Brushed finish
Brushed finish creates a textured pattern on metal surfaces, enhancing aesthetic appeal. Suitable for aluminum, copper, stainless steel, and other materials.

Powder coating
Powder coating is applied to the workpiece surface via electrostatic adhesion, then cured at high temperatures to form a dense coating, enhancing the corrosion resistance of metal and plastic surfaces.

Electroplating finish
Metal plating is deposited onto material surfaces through electrolytic processes to enhance corrosion resistance and wear resistance. This technique is suitable for metals and certain plastics.

Black oxidize
A black oxide coating is formed on metal surfaces through chemical oxidation, offering low cost, a simple process, and reduced light reflection.

Alodine
Forms a protective coating on surfaces through chemical conversion, enhancing corrosion resistance and adhesion. Environmentally friendly with excellent conductivity, suitable for aluminum and magnesium alloys.

Heat treatment
By altering the internal microstructure of metallic materials through heating, enhances hardness, strength, toughness, and wear resistance. suitable for metals such as steel, aluminum alloys, copper alloys, and titanium alloys.
Advantage of cnc machining magnesium
Significant Lightweight Advantages
Magnesium alloy has a density of only 1.74 g/cm³ (2/3 that of aluminum, 1/4 that of steel), making it the lightest metal structural material for engineering applications.
Benefits: Parts manufactured using CNC machining can significantly reduce product weight, improving energy efficiency (e.g., electric vehicle range) or portability (e.g., electronic products).
High Machining Precision and Efficiency
CNC Technology Characteristics: Computer programming control achieves micron-level precision (±0.01 mm), enabling the machining of complex curved surfaces, irregularly shaped holes, and other structures that are difficult to achieve with traditional processes.
Efficiency Improvement: Automated machining reduces manual intervention, making it suitable for mass production (e.g., daily production capacity of thousands of mobile phone mid-frames).
Excellent Surface Quality
Magnesium alloy has a low surface roughness after machining (Ra≤0.8μm), allowing it to be directly used for assembly, reducing post-processing steps such as polishing and sandblasting, and lowering overall costs.
Excellent Heat Dissipation Performance: Magnesium alloys have a thermal conductivity of 156 W/(m·K) (1.5 times that of aluminum). The precision CNC-machined structure optimizes heat dissipation paths, making it suitable for high-power-density applications (such as 5G base stations and gaming laptops).
Electromagnetic Shielding Performance: Magnesium alloys offer excellent shielding against electromagnetic waves. The CNC-machined sealing structure further enhances shielding efficiency, meeting the anti-interference requirements of electronic devices.
High Recyclability: Magnesium alloys have a recycling rate exceeding 95%, and CNC-machined scraps can be 100% recycled and reused, aligning with green manufacturing trends.
Application of cnc machining magnesium
3C Electronics
Applications: Laptop casings, mobile phone frames, tablet stands.
Advantages: Lightweight design improves portability, improved heat dissipation extends device lifespan, and electromagnetic shielding reduces signal interference.
Automotive Industry
Applications: Steering wheel frames, dashboard supports, seat adjustment mechanisms.
Advantages: 10%-15% weight reduction can reduce fuel consumption by 5%-8%; CNC-machined precision structures meet safety standards (such as crash tests).
Aerospace
Applications: Drone arms, satellite structural components, aircraft doors.
Advantages: Every 1kg reduction saves commercial flights over $3,000 in fuel costs annually; CNC-machined lightweight, high-strength structures are key.
Medical Devices
Applications: Portable ultrasound machine casings, surgical robot joints.
Advantages: Excellent biocompatibility; CNC-machined burr-free surfaces reduce infection risk while meeting precision transmission requirements.
Sports Equipment
Applications: Bicycle frames, golf club heads, carabiners.
Advantages: Lightweight design improves motion performance, and the streamlined design spun by CNC machining optimizes aerodynamics.
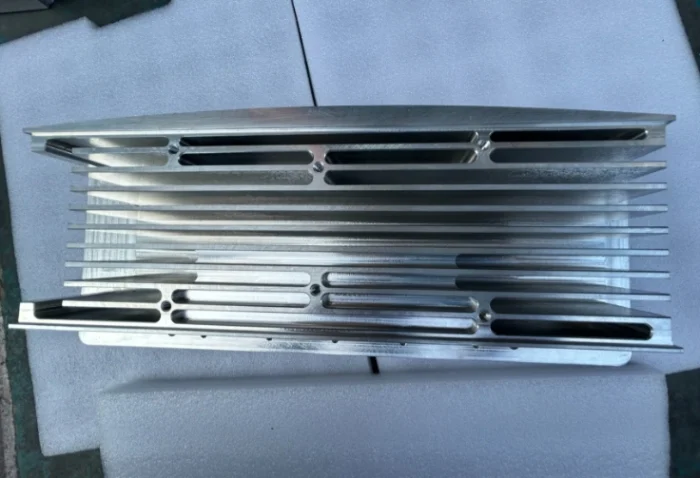
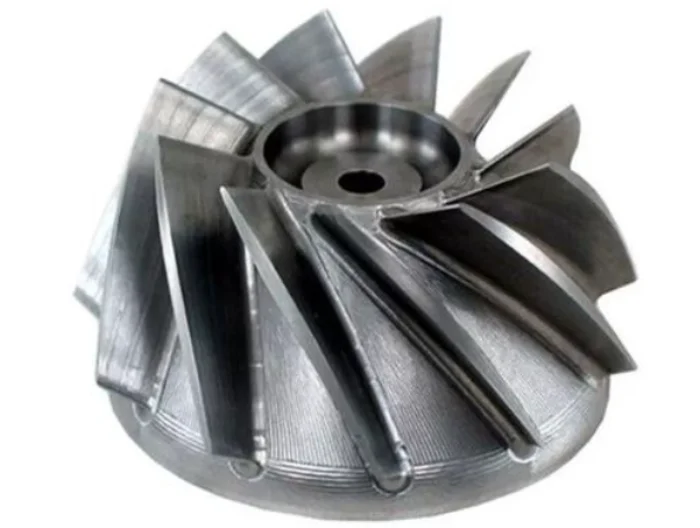





FAQ of cnc machining magnesium
How to select appropriate cutting tools and cutting parameters in CNC machining of magnesium alloys?
Recommended tools are fine-grained or ultra-fine-grained carbide (ISO N / K-type) or diamond-coated tools for mass production, with large rake angle (>10°) and clearance angle (>10°) to reduce cutting force and friction. Magnesium alloys support very high cutting speed (>300 m/min), large feed rate (fz > 0.1 mm/tooth), and large depth/width of cut within machine rigidity. The core principle is to maintain high material removal rate while avoiding local heat accumulation, and toolpaths should ensure continuous cutting, minimize air cutting and sudden stops, with roughing focused on efficiency and finishing focused on precision.
What are some common surface treatment methods after CNC machining of magnesium alloys?
Common surface treatments include chemical oxidation for low-cost basic protection, anodizing for improved corrosion and wear resistance, micro-arc oxidation (MAO) for thick ceramic coatings in harsh environments, electroplating (Ni/Cu/Cr) for decorative or functional purposes after proper pretreatment, and advanced self-healing composite oxidation coatings that provide very high corrosion resistance (up to 500–1000 hours salt spray) for high-end applications.
Does CNC machining of magnesium alloys pose safety risks? How can these be mitigated?
Magnesium alloy chips and dust can ignite at high temperature (around 500°C), so wet cutting with emulsion or oil mist is recommended to reduce heat, machines should be equipped with fire suppression and dust collection systems, compressed air should not be used to blow chips, chips must be cleaned regularly, and flame-retardant magnesium alloys (such as Ca/Sr-modified AZ series) should be prioritized to reduce fire risk.

